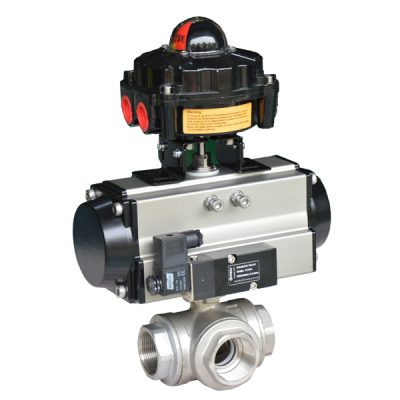
A three way valve is an essential component in fluid control systems, designed to direct or mix flow between three distinct ports. Whether it’s a 3 way ball valve t port for precise directional control or a 3 way stainless steel ball valve for high-pressure, corrosion-resistant applications, this valve type offers versatility and efficiency. From 3 way ss ball valves to a ball valve 3 way configuration, these valves provide reliable performance in industries like chemical processing and HVAC systems. Each design, such as the 3 three way ball valve, serves specialized needs, making three way valve? indispensable in tailored system solutions.
Introduction three way valve?
A three way valve is a vital component in fluid management systems, designed to manage flow direction and control efficiently. Common configurations, such as the 3-way ball valve or ball valve 3 way t port, provide flexibility for mixing or diverting flows. A stainless 3 way ball valve, known for its durability and resistance to corrosion, is commonly used in demanding environments. Whether in industrial setups or specialized systems, 3way ball valves and other three way ball valves adapt seamlessly to varied applications, exemplifying their precision and utility.
Brief overview of what a three-way valve is and its importance in industrial applications.
A three-way valve is a device used to control and direct fluid flow between three ports in a system. It is commonly employed in industrial applications to manage processes such as fluid mixing, flow diversion, or system switching without the need for additional components. This valve type allows for precise control of fluid pathways, improving overall system functionality and efficiency. Its design makes it suitable for industries like chemical processing, HVAC, and water treatment, where managing fluid direction or combining flows is essential for operation.
Highlight its versatility in controlling fluid flow in multiple directions.
A three-way valve is designed to regulate and direct fluid flow between three distinct pathways, providing multiple options for fluid control in a single system. It enables the combination, separation, or diversion of flows without the need for additional components. By allowing fluids to move in multiple directions as needed, the valve streamlines system operations and supports processes that require flexible pathways. This functionality makes it an essential part of systems where controlling the direction of fluid flow is critical for proper operation.
Mention its relevance across various systems requiring precise flow control.
A three-way valve plays a critical role in systems that require precise flow control by efficiently managing the direction, combination, or separation of fluids. It is integrated into processes across industries such as chemical manufacturing, HVAC, and water treatment, where maintaining specific flow paths is crucial for system operations. The valve’s ability to adjust flow pathways supports the functionality of systems that rely on accurate control, making it essential for ensuring efficient and consistent performance in diverse applications.
Understanding the Basics of a Three-Way Valve
Define a three-way valve and its core function.
A three-way valve is a mechanical device used to control and direct fluid flow through three connected ports. Its core function is to either divide, combine, or switch fluid pathways in a system, depending on the specific configuration and operational requirements. By enabling the redirection or blending of fluids within a single unit, it simplifies system design and enhances the management of flow processes across a range of applications.

Explain the three ports and how they enable switching, mixing, or diverting the flow.
A three-way valve is designed with three ports that serve as entry and exit points for fluid flow. These ports allow the valve to perform different control functions within a system. Switching is achieved by directing the flow between two chosen ports, depending on the desired pathway. Mixing occurs when fluids from two ports combine into a single outlet, creating a merged flow. Diverting separates fluid from one inlet into two different outlets, enabling fluid redirection. This configuration makes the valve adaptable to functional requirements in various systems.

Types of Three-Way Valves
Overview of different types of three-way valves and their specific applications.
Diverting three-way valve for directing fluid from one inlet to two outlets.
A diverting three-way valve features a single inlet and two outlets, designed to direct fluid flow from the inlet to one of the two separate outlets as required. By adjusting the valve’s internal mechanism, the flow path can be controlled to switch between the outlets, ensuring proper redirection within the system. This type of valve is commonly used in applications that require distribution of a single fluid source to different destinations, such as in process systems, cooling circuits, or fluid distribution networks. Its ability to manage flow transitions makes it a key component in systems requiring precise fluid allocation.
Mixing three-way valve for blending fluid from two inlets into one outlet.
A mixing three-way valve is designed with two inlets and one outlet, allowing it to combine fluids from two sources into a single flow. By regulating the valve’s internal components, it controls the proportion of each input, ensuring the desired mixture is achieved before the fluid exits through the outlet. This type of valve is commonly utilized in systems requiring precise fluid blending, such as heating processes, chemical mixing operations, and temperature regulation systems. Its functionality supports processes that depend on controlled merging of inputs for consistent output performance.
L-port and T-port valve configurations and their practical uses.
L-port and T-port valve configurations refer to the internal flow pathways within a three-way valve. The L-port configuration allows fluid to flow between two of its three ports at a time, forming an “L”-shape pathway. This design is used to switch or isolate flow between two different channels, commonly found in systems requiring cyclical redirection or isolation. The T-port configuration, on the other hand, enables fluid to flow between all three ports simultaneously or selectively block one port while maintaining flow between the other two. This makes it suitable for mixing or diverting flow paths in more complex operations, often applied in distribution systems or processes needing flexible control of multiple fluid pathways. Both configurations provide specific functionality for diverse system requirements.
How a Three-Way Valve Works
Breakdown of the operational mechanics of a three-way valve.
A three-way valve operates by controlling fluid flow through its three interconnected ports using an internal mechanism such as a ball, plug, or disc. This mechanism rotates or shifts within the valve body to direct the flow between the ports. When positioned appropriately, the valve can mix, divert, or switch fluid paths based on system requirements. The internal mechanism is activated manually or automatically, using actuators such as pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic systems. This design allows precise control over the flow paths, enabling the valve to handle multiple operational scenarios in fluid management systems.

Explanation of flow path control using valve actuators or manual systems.
Flow path control in a three-way valve is achieved using either manual systems or valve actuators. A manual system involves direct operation through levers or handles to adjust the valve’s internal mechanism, determining the direction of fluid flow. Valve actuators, on the other hand, automate this process by using pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic power to adjust the valve’s position. These actuators are often integrated with control systems to execute specific flow commands, ensuring accurate alignment of the internal mechanism for tasks such as mixing, diverting, or switching flow paths. Both methods enable the valve to respond to operational demands within a fluid management system.
Highlight how sealing and internal components ensure leak-free operation.
The sealing and internal components of a three-way valve are designed to maintain fluid integrity and prevent leaks during operation. Seals, often made from materials such as elastomers, PTFE, or metal, are strategically placed around critical areas like the valve stem, ports, and internal mechanism. These seals create barriers that block fluid from escaping the valve or migrating between unintended pathways. The internal components, including the ball, plug, or disc, are engineered with consistent surface finishes and precise tolerances to ensure tight contact with the seals. This combination of robust sealing and precise internal design enables the valve to sustain reliable performance in various pressure and flow conditions.
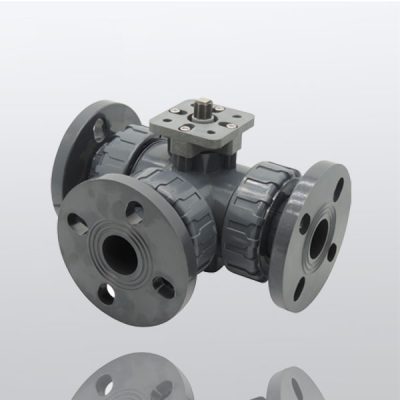

Applications of Three-Way Valves in Industrial Systems
Common industries utilizing three way valve?.
Three-way valves are utilized across various industries to manage fluid flow and enhance operational control. The oil and gas industry employs these valves for processes such as blending, diverting, and switching flow in pipelines. The chemical and petrochemical sectors use them for precise mixing and temperature regulation in reaction or storage systems. Water treatment facilities deploy these valves to regulate distribution between different processing units. The HVAC industry uses them to control heating or cooling outputs in temperature management systems. Additionally, food and beverage processing relies on three-way valves for transferring and mixing liquids in production lines. These applications underscore the role of three-way valves in supporting diverse industrial operations.
Usage scenarios like temperature regulation, flow reversal, and pressure control.
Three-way valves are used in industrial systems for various operational scenarios such as temperature regulation, flow reversal, and pressure control. Temperature regulation is achieved by mixing or diverting hot and cold fluid streams to maintain desired thermal conditions in processes like chemical reactions or HVAC systems. Flow reversal is implemented in systems requiring periodic directional changes, such as pipeline cleaning or alternating flows between storage tanks and processing units. For pressure control, these valves manage distribution or isolation of fluids to maintain consistent pressure levels in systems like hydraulic machinery or compressed air networks. These usage scenarios demonstrate the functionality of three-way valves in critical industrial operations.
Materials and Design Features in Three Way Valve
Discuss common materials such as stainless steel, brass, or PVC based on media compatibility.
The selection of materials for three-way valves is based on media compatibility and operational requirements within specific applications. Stainless steel is widely used for its ability to handle corrosive and high-temperature fluids, making it suitable for industries like chemical processing and oil and gas. Brass is commonly chosen for its resistance to water and non-corrosive liquids, making it practical for plumbing and HVAC systems. PVC is selected for its compatibility with various chemicals and its effectiveness in low-pressure applications like water treatment and irrigation. By matching materials to the properties of the media, three-way valves ensure long-term performance and reliability in diverse operating environments.

Highlight essential design features, including corrosion resistance and temperature tolerance.
Three-way valves incorporate design features such as corrosion resistance and temperature tolerance to ensure reliable performance in diverse applications. Corrosion resistance is achieved through the selection of materials like stainless steel or specialized coatings that protect internal components from degradation caused by exposure to corrosive media. Temperature tolerance is ensured by using materials and sealing solutions capable of withstanding thermal stress in high- and low-temperature environments. These features enable three-way valves to maintain operational integrity and functionality under challenging conditions, supporting consistent and efficient performance across various industrial systems.
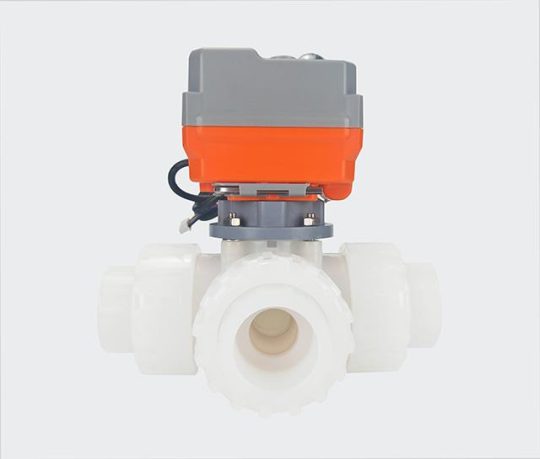

Benefits of Using a Three Way Valve?
Increased efficiency and flexibility in system design.
Three way valve? contribute to efficiency and flexibility in system design by combining multiple functions into a single unit, reducing the need for additional components. They enable processes such as mixing, diverting, and flow control within a compact setup, simplifying system layouts and reducing installation requirements. Their ability to handle multiple roles facilitates seamless adjustments and transitions in operations, supporting systems that require frequent changes in flow direction or rate. These operational benefits optimize resource usage and improve the adaptability of systems, making them suitable for dynamic industrial environments.
Reduction in the need for additional piping and connectors.
Three way valve? reduce the need for additional piping and connectors by combining multiple flow paths within a single unit. This consolidation decreases the complexity of system layouts, limiting the amount of external connections required for mixing, diverting, or flow control. Fewer components translate to lower material costs, reduced installation time, and simpler maintenance, as there are fewer potential points for leaks or failures. This streamlined design supports more efficient resource use and enhances the operational reliability of industrial systems.
Cost-effectiveness compared to other multi-valve configurations.
Three way valve? offer cost-effectiveness compared to other multi-valve configurations by consolidating multiple functions into a single unit. This reduces the need for purchasing and installing multiple valves, lowering upfront costs and minimizing the amount of space required in system layouts. The simplified design also decreases installation and maintenance expenses, as there are fewer components to manage and fewer potential points of failure. By streamlining operational requirements, three way valve? help reduce overall system costs while maintaining functionality and efficiency in industrial applications.
Selection Criteria for Choosing the Right Three Way Valve?s
Factors to consider during selection.
When selecting a three way valve?, factors such as media compatibility, pressure and temperature requirements, and operational needs should be evaluated. Media compatibility ensures the selected materials do not degrade or react with the substances being handled. Pressure and temperature requirements determine the valve’s ability to function safely within the system’s operating conditions. Operational needs, including the desired flow patterns and control mechanisms, help identify the appropriate design and actuation method for the application. Assessing these factors ensures proper integration and reliable performance in the system.
Importance of compatibility with system requirements and operational conditions.
Compatibility with system requirements and operational conditions is a critical factor when selecting a three-way valve. Ensuring compatibility prevents material degradation, improper functionality, or system strain caused by mismatched specifications. Matching the operating pressure and temperature ranges of the valve with the system ensures safe operation and reduces the risk of failure. Proper alignment with flow control demands and media type contributes to efficient and reliable performance. Evaluating these aspects ensures the valve operates as intended and supports the overall effectiveness and safety of the system.
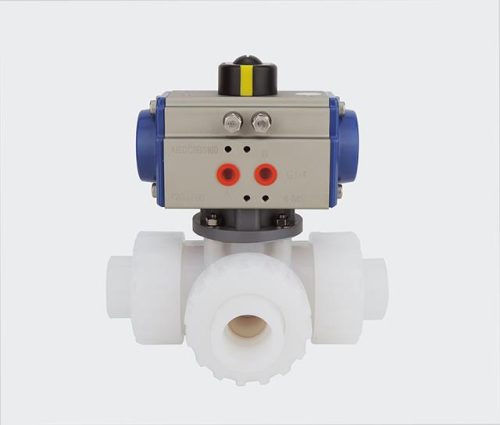

Maintenance and Troubleshooting of? Three Way Valve?
General maintenance tips to ensure longevity and reliable performance.
Regular inspections of three way valve? are essential to identify potential issues such as leaks or blockages. Cleaning the valve components helps ensure unobstructed flow and prevents buildup that could compromise functionality. Lubricating moving parts maintains smooth operation and reduces wear from friction. Replacing worn or damaged components, such as seals or seats, in a timely manner prevents minor issues from escalating. Monitoring system performance and addressing irregularities promptly supports consistent operation and helps extend the valve’s service life.
Addressing common issues like leaks, wear on seals, and actuator malfunctions.
Identifying and addressing common issues in three-way valves maintains functionality and reduces downtime. Leaks can be managed by inspecting seals and connections, tightening fittings, or replacing damaged seals. Wear on seals can be minimized by selecting materials suitable for the operating conditions and replacing seals promptly when degradation is observed. Actuator malfunctions can be resolved by checking for misalignment, ensuring proper electrical or pneumatic connections, and replacing worn-out components. Regular maintenance schedules that include these checks help prevent recurring issues and ensure reliable valve operation.
FAQ three way valve?
Q1: What are 3 way valves, and how are they used?
A1: 3 way valves are designed to control the flow of media through three ports, allowing for processes like mixing, diverting, or shutting off flow in industrial systems. They are commonly used to simplify piping systems and provide efficient flow control, especially in applications where multiple lines need to connect seamlessly.
Q2: How does a 3-way valve differ from other valves, and what is a three way ball valve?
A2: Unlike standard valves that control flow in one direction, a 3-way valve has three ports that can be arranged for specific flow patterns. A three way ball valve, in particular, uses a rotating ball with a machined pathway to either mix media from two sources or divert flow between different outlets. Its versatility makes it a popular choice in industries like chemical processing and HVAC systems.
Q3: What are the functions of a T port valve in 3-way valve configurations?
A3: A T port valve is a type of 3-way valve where the internal ball is designed in the shape of a “T.” This design allows the valve to connect all three ports simultaneously or direct flow between selected ports, making it ideal for applications that require mixing or bypass modes within the system.

Conclusion three way valve?
A three way valve? is a versatile component used to control the flow of media through three interconnected ports, offering solutions for mixing, diverting, or shutoff functions in various systems. Different designs, such as the 3 three way ball valve and ball valve 3 way configurations, provide flexibility for specific applications. For example, the 3 way ball valve t port allows mixing or selective flow control based on system needs. Materials like stainless steel make variants such as the 3 way ss ball valve and 3 way stainless steel ball valve ideal for handling demanding conditions. Overall, the 3 way ball valve remains a critical tool in industries requiring reliable and efficient flow management.

