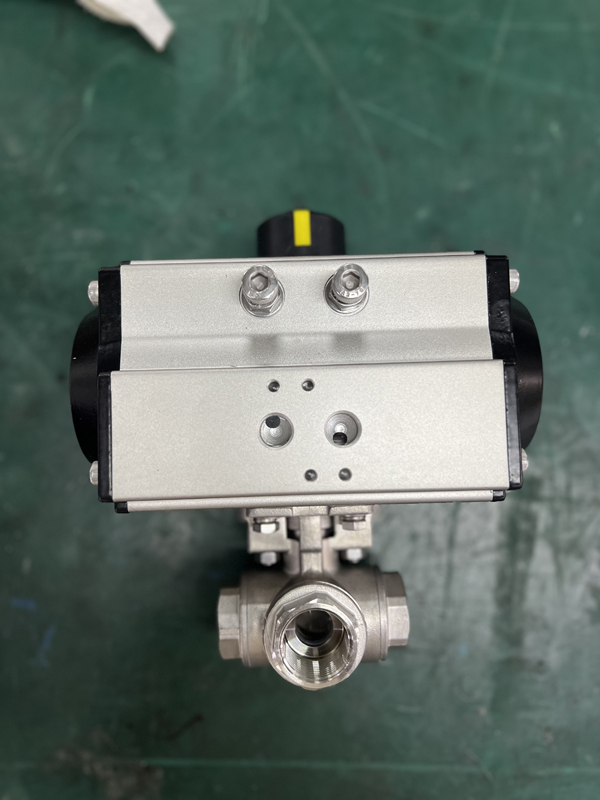
A 3 way ball valve? is a versatile component used extensively for efficient flow control and redirection in piping systems. With its unique design, this type of valve features three ports, allowing it to mix, divert, or isolate flows as needed. Available in various configurations, such as the 3 way ball valve? t port, it offers flexibility for a range of operations. Built from durable materials like stainless steel, options such as the 3 way ss ball valve or 3 way stainless steel ball valve provide enhanced corrosion resistance and reliability in demanding environments. Understanding the workings of a 3 three way ball valve, including its internal mechanics, is essential for selecting the right ball valve 3 way solution for specific applications.
Introduction 3 way ball valve?
A three way valve, commonly known as a 3-way ball valve, is a practical solution for efficiently managing and controlling fluid flow in a variety of applications. Designed with three ports, these versatile components can perform tasks such as mixing, diverting, or completely shutting off flow. Variants like the ball valve 3 way t port and stainless 3 way ball valve? are particularly popular in systems requiring durability and precision. Understanding the functionality of 3way ball valves is key to selecting the right option, as three way ball valves offer exceptional adaptability for complex flow control systems.

Brief overview of what a 3-way ball valve is.
A 3-way ball valve is a valve designed with three ports that control the direction of fluid flow in a system. It functions by using a rotating ball with a bore to manage the flow path between the ports. The valve is typically used for mixing flows, diverting flow between different channels, or isolating flow in a system. It is available in different configurations, such as T-port and L-port, to accommodate various operational requirements.
Importance of 3-way ball valves in flow control systems.
3-way ball valves play a critical role in flow control systems by allowing fluid to be directed, mixed, or isolated between different channels. These valves enable the efficient management of flow paths, reducing the need for multiple valves in complex systems. Their design supports versatile configurations, such as T-port or L-port, to meet operational demands in applications like fluid distribution, process control, and system maintenance. By simplifying system layouts and providing reliable control, they contribute to streamlined operations in a range of industries.
Understanding the Working Mechanism of a 3-Way Ball Valve
Detailed explanation of the valve’s structure.
A 3-way ball valve consists of a body, a rotating ball, three ports, and a stem that connects the ball to an external actuator or handle. The ball has a bore that aligns with the ports to control fluid flow. The ports are arranged in either T-port or L-port configurations, allowing for different flow paths depending on the system’s requirements. Seals are placed around the ball to prevent leaks, and the stem ensures controlled rotation of the ball to open, close, or redirect flow. The valve body houses all components and provides the structural framework for connection to pipelines.
How the ball rotates to control the flow direction.
The ball in a 3-way ball valve rotates within the valve body to control the flow direction through its ports. The ball contains a bore, which is a hollow passage that aligns with the valve’s ports to direct or redirect fluid. When the external actuator or handle is rotated, it moves the stem, which in turn rotates the ball. Depending on the ball’s position, the bore can align with two of the three ports to allow flow, block one port to isolate a section, or redirect flow between two channels. The T-port or L-port configuration of the ball determines the specific flow paths that can be achieved.

Description of the flow paths.
T-port
A T-port configuration in a 3-way ball valve features a ball with a bore shaped like the letter T. This design allows fluid to flow through any two of the three ports simultaneously or through all three ports at once, depending on the position of the ball. The T-port configuration is commonly used for mixing flows from two sources, distributing fluid to two different channels, or creating bypass loops in a system. The functionality depends on how the ball is positioned within the valve and whether the flow needs to be combined, diverted, or isolated.
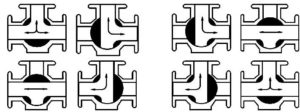
L-port configurations
An L-port configuration in a 3-way ball valve includes a ball with a bore shaped like the letter L. This design enables fluid flow between two of the three ports, while the third port remains isolated. The L-port configuration is utilized primarily for diverting flow from one channel to another or for switching between two separate fluid paths. By rotating the ball within the valve, users can control which ports are connected, redirecting the flow to meet specific system requirements. The arrangement ensures precise flow management in processes requiring separation or redirection of fluids.

Types of 3-Way Ball Valves
Explanation of T-port and L-port 3-way ball valves and their differences.
T-port and L-port 3-way ball valves differ in their internal bore configurations and how they manage fluid flow. A T-port valve has a bore shaped like a T, allowing fluid to flow through all three ports simultaneously or between any two of the ports. It is suitable for operations requiring mixing of fluids, distribution to multiple channels, or bypass loops. An L-port valve, with its L-shaped bore, only connects two of the three ports at a time, leaving the third port isolated. This configuration is used to divert flow between two paths or to switch between separate fluid channels. The selection between T-port and L-port depends on the system’s operational and flow control requirements.
Directional flow operations for each type.
Directional flow operations for T-port and L-port 3-way ball valves are determined by the shape of their internal bores and the alignment of the ball within the valve. A T-port valve allows flow to be directed through two ports simultaneously, or all three ports at once, depending on the orientation of the ball. This makes it suitable for applications requiring fluid mixing, distribution to multiple outlets, or the creation of bypass paths. An L-port valve directs flow between two of the three ports at a time, isolating the third port in each configuration. This design is used to alternate between two separate paths or to switch flow direction based on system requirements. The operational configuration of each valve type ensures specific flow management tailored to different process needs.
Examples of scenarios where each type is best suited.
T-port and L-port 3-way ball valves are used in different scenarios based on their flow control capabilities. A T-port valve is suitable for applications requiring the mixing of fluids, such as combining two input streams into one or distributing a single input to two separate outlets. It is also used for creating bypass loops in systems where flow needs to be redirected without disrupting operations. An L-port valve is commonly used in systems that require alternating between two separate flow paths, such as switching supply from one tank to another or directing flow between two different processes. These configurations provide tailored flow management for specific operational needs.
Key Applications of 3-Way Ball Valves
Industries that rely on 3-way ball valves.
Industries that rely on 3-way ball valves include chemical processing, where they are used for mixing, redirecting, or isolating fluid flows in reaction and storage systems. They are common in the oil and gas industry for applications like fluid diversion in pipelines or switching between storage tanks. The food and beverage industry uses them for controlling the flow of liquid ingredients during production processes. Water treatment plants incorporate them in systems for redirecting water flow or managing filtration processes. Additionally, HVAC systems use 3-way ball valves for temperature control and flow redirection in heating and cooling circuits. These valves provide operational support across diverse industrial applications.
Explanation of common use cases such as flow diversion, mixing, and shutoff.
3-way ball valves are used for flow diversion, mixing, and shutoff in various systems. Flow diversion involves redirecting a fluid from one port to another, making it suitable for switching between pipelines or directing input to multiple destinations. Mixing applications use these valves to combine fluids from two ports into a single outlet, often seen in processes requiring blended outputs, such as chemical or food production. For shutoff purposes, the valve isolates a portion of a system by stopping the flow to one or more ports, which is crucial during maintenance or process adjustments. These functions enable efficient control and management of fluid flows in system operations.
Addressing the importance of material selection based on the application.
Material selection for 3-way ball valves is crucial to ensure compatibility with the operating environment and fluid type. Metallic materials like stainless steel are commonly used in applications involving corrosive fluids, high temperatures, or high pressure due to their resistance to degradation. Plastics such as PVC or CPVC are selected for systems handling non-corrosive fluids, lower pressures, or specific chemical compositions, often found in water treatment or lightweight piping applications. Elastomers and seals within the valve must also match the fluid characteristics to prevent leaks or premature wear. Proper material selection ensures that the valve performs reliably, meets the system’s operational requirements, and minimizes maintenance or replacement needs.
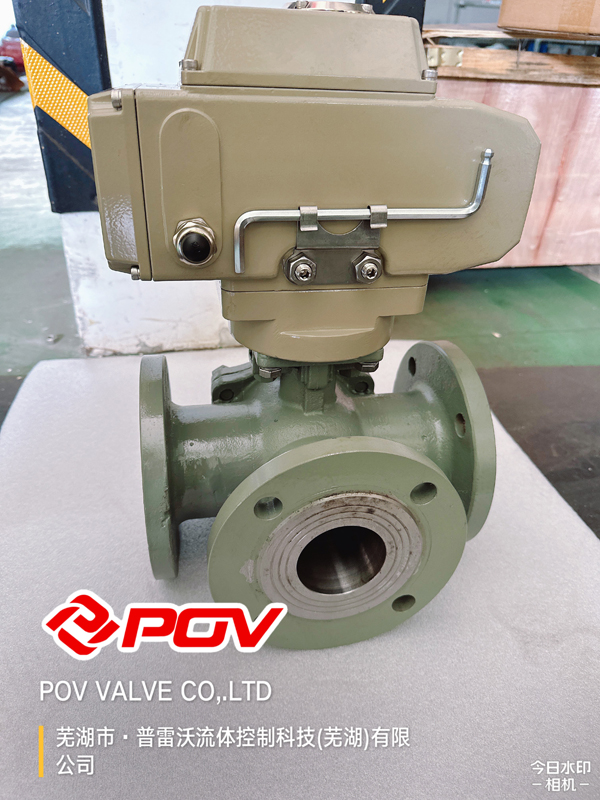

Advantages of Using a 3-Way Ball Valve
Efficient flow control with fewer connections compared to multiple valves.
3-way ball valves enable efficient flow control by integrating multiple flow paths within a single valve body, reducing the need for multiple valves and connections. This design allows operations such as diverting, mixing, or isolating flows to be performed with fewer system components. Fewer connections minimize potential leak points and simplify installation, maintenance, and system configuration. The consolidated structure supports streamlined piping layouts, reduces installation time, and decreases overall material costs. Using one valve to perform multiple functions improves efficiency while maintaining effective control over fluid direction and distribution.
Compact design for space-saving installations.
The compact design of 3-way ball valves provides practical benefits for space-saving installations by combining multiple flow control functions into a single unit. This reduces the overall footprint of the piping system and allows for installation in areas with limited space. The reduced need for additional valves or extended piping layouts simplifies system design and supports efficient use of available space. The streamlined configuration also minimizes installation complexity and contributes to the effective management of flow direction and mixing in tight operational environments.
Versatility in handling various media types.
3-way ball valves are designed to handle a wide range of media types, including liquids, gases, and slurries, making them suitable for diverse applications. Their internal construction supports compatibility with different flow properties, pressures, and temperatures. This versatility is enhanced by the availability of various material options for valve components, ensuring compatibility with corrosive or abrasive substances when required. The ability to adapt to diverse media types simplifies system design and reduces the need for specialized valves in multi-purpose operations, making these valves an efficient choice for systems that handle multiple media.
Low maintenance and robust performance.
3-way ball valves are designed to provide reliable performance while requiring minimal maintenance. Their simple and durable construction reduces the risk of wear and mechanical failure, even in demanding operating conditions. The use of high-quality materials for seals and internal components helps minimize degradation, ensuring consistent operation over time. The reduced need for maintenance lowers operational downtime and associated costs, making them an efficient option for systems requiring long-term reliability. These valves are engineered to handle repetitive operations and varying flow conditions without compromising functionality, supporting consistent system performance.
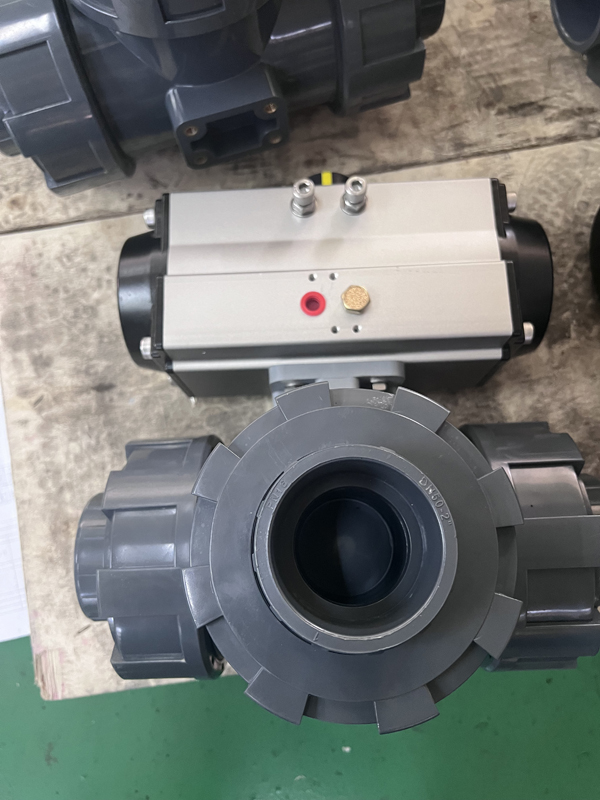

Factors to Consider When Selecting a 3-Way Ball Valve
Importance of choosing the right size, materials, and pressure rating.
Selecting the appropriate size, materials, and pressure rating for a 3-way ball valve is essential to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with the system. The valve size must align with the flow requirements to prevent restrictions or excessive pressure drops. Choosing materials that match the properties of the medium and the operating environment is crucial to avoid corrosion, erosion, or chemical reactions that could compromise valve integrity. The pressure rating must accommodate the system’s operating pressure to prevent structural issues and ensure consistent functionality. Careful consideration of these factors ensures the valve meets the operational and safety requirements of the application.
Understanding compatibility with the intended media.
Understanding compatibility with the intended media is critical when selecting a 3-way ball valve to ensure reliable performance and durability. The valve materials must resist potential degradation caused by the physical and chemical properties of the media, such as abrasiveness, corrosiveness, or viscosity. Failure to align material properties with the media can lead to wear, leakage, or chemical reactions that compromise system efficiency. Additionally, seals and internal components must support the temperature and pressure ranges of the media to maintain operation without failure. Evaluating media compatibility helps to reduce maintenance requirements and extends the lifecycle of the valve in its application.
Ensuring the valve meets industry standards and certifications.
Ensuring a 3-way ball valve meets industry standards and certifications is essential for achieving compliance with safety, reliability, and regulatory requirements. Adherence to recognized standards confirms that the valve has been tested for consistent performance and structural integrity under defined conditions. Certifications demonstrate that the valve design, materials, and manufacturing processes comply with regulatory guidelines applicable to specific sectors, such as chemical processing, pharmaceutical production, or oil and gas operations. Compliance reduces the risk of system failure and ensures compatibility with operational requirements, while also meeting legal and insurance obligations for the installed equipment.

FAQ 3 way ball valve?
1. What is the function of a three way ball valve, and how does it operate?
A three way ball valve is a type of 3 way valve designed to direct flow between three different ports. The operation relies on a rotating ball inside the valve that has a drilled passage, which aligns with or blocks the flow channels depending on its position. This allows 3 way valves to distribute, mix, or divert the flow of liquids, gases, or other media in pipelines. A T port valve configuration is specifically used for mixing or distributing flows to multiple directions.
2. How does a T port valve differ from other 3-way valve configurations?
A T port valve is a variation of a 3 way valve that features a ball with a T-shaped internal path. This design allows the valve to divert flow to two outlets simultaneously or connect three ports together in a mixing operation. Unlike a standard 3-way valve with an L port, which only directs flow between two ports at a time, the T port valve provides more versatile flow control, making it suitable for applications requiring simultaneous distribution.
3. Can 3 way valves support bi-directional flow, and how is that managed?
Yes, 3 way valves, including the three way ball valve, can support bi-directional flow depending on the internal ball design and port configuration. For instance, a T port valve can direct flow from one inlet to two outlets or allow flow from two inlets to mix into a single outlet. The operator changes the position of the ball manually or with an actuator to adjust the flow paths, ensuring efficient control in systems requiring flexible flow routes.

Conclusion 3 way ball valve?
Understanding how a 3 way ball valve? functions provides valuable insight into its role in flow control systems. The 3 three way ball valve offers efficient management of liquid and gas distribution through its versatile design. Whether using a ball valve 3 way configuration for directional control or the 3 way ball valve? t port for mixing or distributing flows, these valves are essential in various applications. Options like the 3 way ss ball valve and 3 way stainless steel ball valve further expand their usability, particularly in demanding environments that require corrosion resistance and durability. The 3 way ball valve remains a reliable and adaptable component in system design, supporting precise and efficient operations.

